Simplifying
Shoulder Surgery
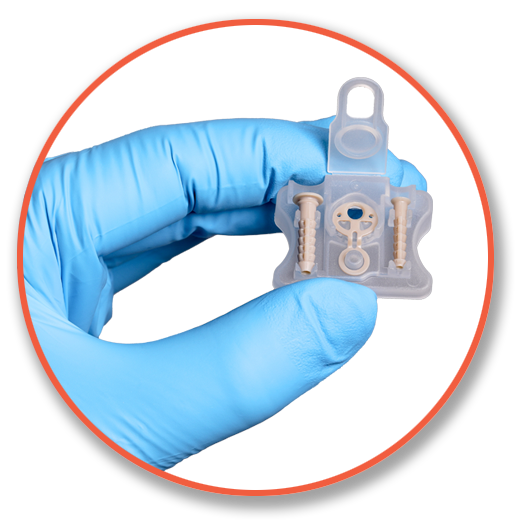
The SINEFIX™ implant was designed to replace traditional suture anchors that require complex and time-consuming steps and address the shortcomings of suture-based fixation.
SINEFIX represents a completely different approach to rotator cuff repair. Instead of threads cutting through tendon, it uses a small polyether-ether-ketone (PEEK) implant that effectively “staples” the tendon to bone over a broad area. The implant consists of a base plate with teeth on the underside that sits on the tendon surface and small fixation prongs that are driven into bone, clamping the tendon down.
The SINEFIX design is aimed at eliminating the point-loading of sutures—there are no concentrated suture anchor points, and at distributing the pressure is evenly across the repair footprint.


FDA Cleared
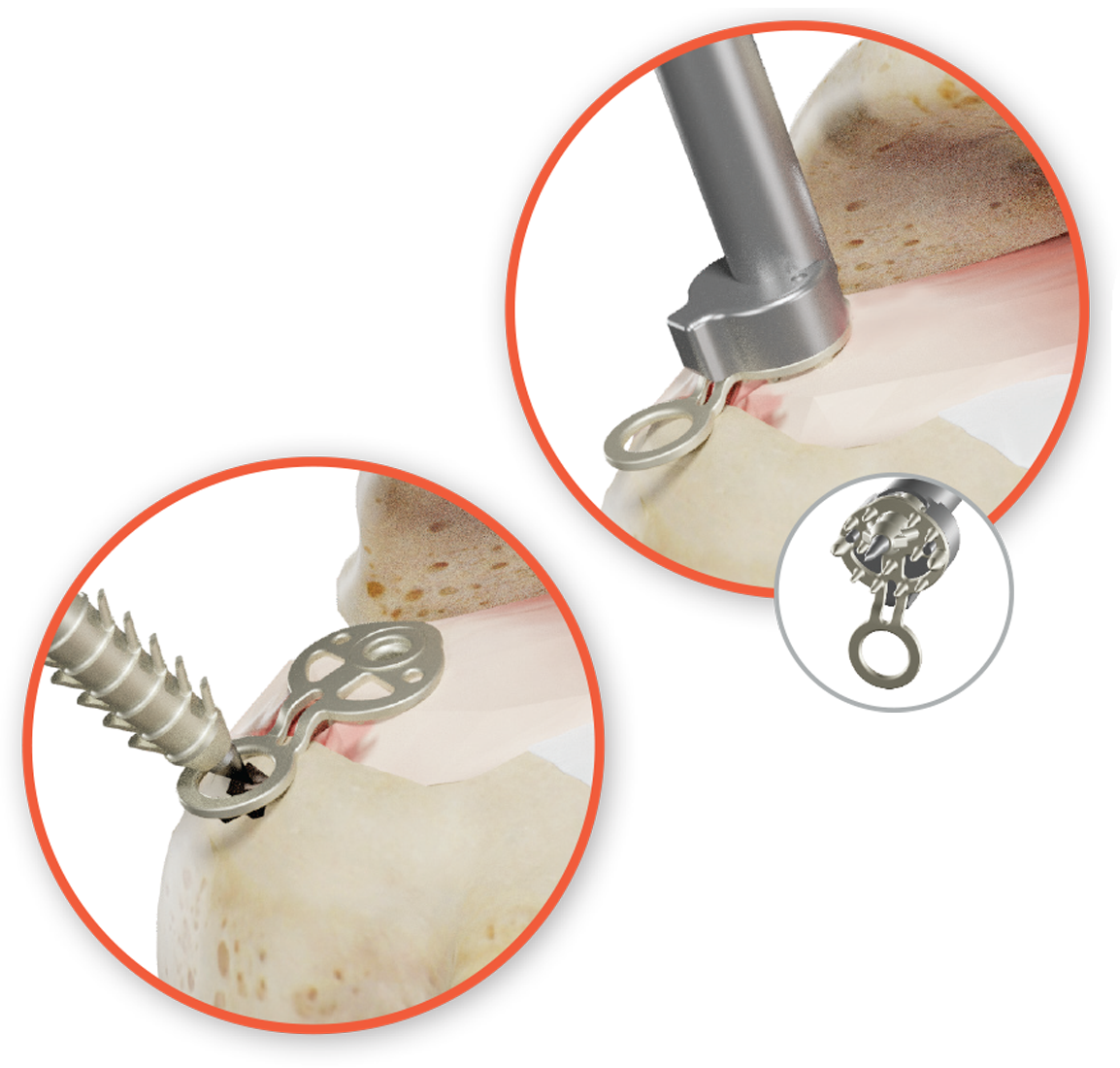
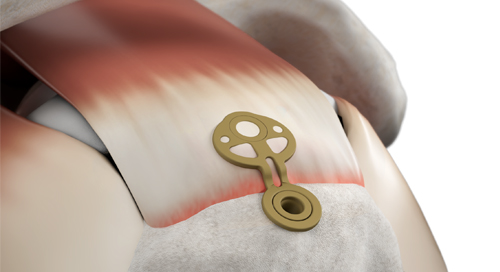
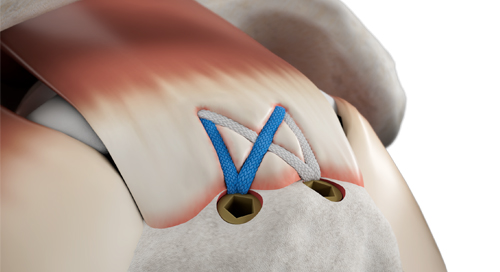
Simple Surgical Technique
- No knot tying or suture management required
- One SINEFIX implant can replace multiple suture anchors
- Expected to reduce surgery time and contribute to cost savings
Improved Tendon to Bone Fixation
- Higher pull-out forces than double row fixation using less implants
- Minimizes punctual pressure aiming to reduce risk of loosening post surgery
- Demonstrates less gap formation than double row fixation to optimize contact pressure
Ensuring blood flow and facilitating healing
- Gentle contact between tendon and bone aiming to prevent the creation of any acellular, necrotic zones in the tendon
- Even pressure load over the tendon ensuring good blood circulation
- Instrumentation designed to prevent excessive compression of tendon
BIOMECHANICAL EVALUATION
In a direct comparison, the new SINEFIX implant had higher pull-out forces and less gap formation than a double-row repair (DDR). 10 fresh sheep infraspinatus tendons were refixed with SINEFIX and DRR (2x medial and 1x lateral all-suture anchor) respectively.
Methodology: after preloading with 10 N, the tendons were cyclically loaded with 10 to 62 N over 200 cycles at 0.2 Hz. The tendons, which were then still refixed, were loaded until they ruptured. View the poster.
Gap Formation:
Gap formation under cyclic loading up to 62 N
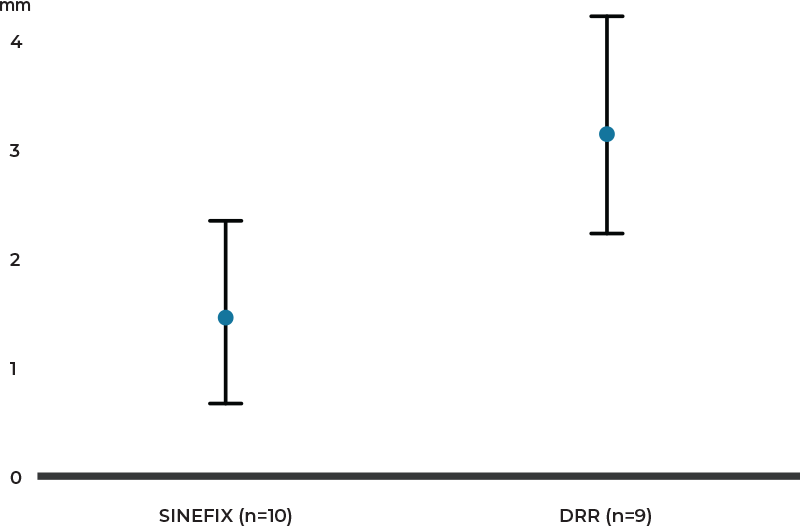
All (n=10) tendons refixed with SINEFIX survived cyclic loading up to 62N with a gap formation up to 1.49 millimeter (SD 0.84). In contrast, with the DRR method, one tendon remained less stable (n=9) with a gap formation of 3.19 millimeters (SD 0.91) (p=0.001).
Pullout Strength:
Pullout forces
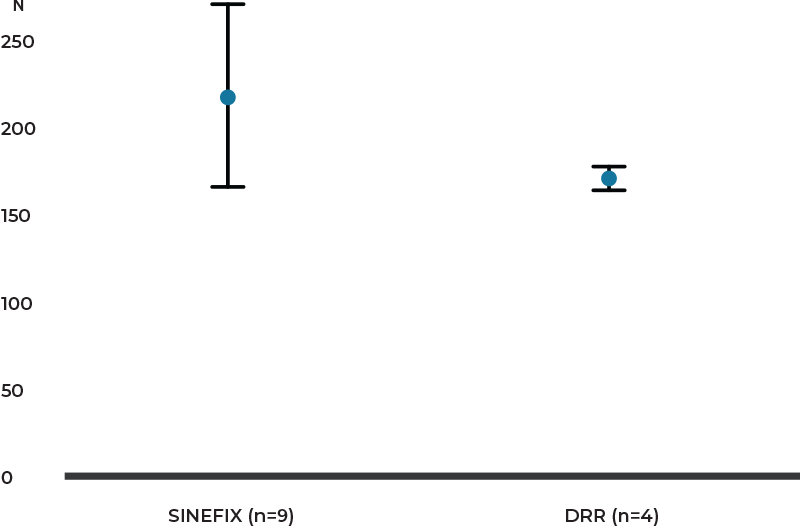

The maximum pullout forces with SINEFIX (n=6) were 215N (SD 55) versus DRR (n=4) with 166N (SD 15) (p=0.084).
Designed to address challenges with rotator cuff repair surgery
Learn more about SINEFIX and the three main challenges with rotator cuff repair surgery it addresses.
